The Internet of Things (IoT) unlocks many possibilities but comes with huge security risks. IoT focused cyber-attacks have already become widespread. Attackers may gain entry to the network using a compromised device, or commandeer the device to do their bidding. The Dyn attack, where cybercriminals compromised cameras and other gadgets connected to the ISP’s network, is a portent of things to come.
96% of security professionals expect an increase in IoT breaches. But there is no single magic bullet to fix IoT security issues. Enterprises with IoT networks invest in a mix of IoT security tools and technologies.
1. Network Security Tools
Traditional antivirus, anti-malware, and firewalls hold good for IoT.
Securing endpoints and configuring the deployments secures the IoT network. But network security in IoT is challenging compared to traditional network security. Networks connecting IoT devices to back-end systems use diverse communication protocols and standards.
Bayshore Networks, Bastille, Cisco, and Darktrace, among others, offer IoT focused solutions.
Bayshore Networks’s automated Learning Engine leverages threat intelligence sources well. The suite offers timely threat alerts.
Bastille’s cloud-based platform identifies and mitigates threats from RF-enabled devices. The platform supports 100+ distinct communication protocols, to secure wireless communication protocols.
2. Network Monitoring
IoT devices come in different shape, size, and function. Many devices are resource-constrained in power, performance, and functionality. Many devices function on customized and non-standard operating systems, not recognized by standard security systems. A case in point is the very vulnerable NANIX, a Linux version for wearable devices. Many connected devices use non-standard and legacy communication protocols such as M2M. The limited memory render devices incapable of patching or software upgrade. Traditional endpoint security models rarely work in such a scenario.
Intrusion prevention and detection systems are critical to secure the IoT ecosystem. Sound network monitoring triggers intrusion alerts and preempts damage.
Bitdefender offers a robust tool to protect smart devices from possible cyber threats. The suite’s unified approach to security integrates PCs, smartphones, smart TVs, Wi-Fi spots and more. Security enforcement is through a vulnerability assessment, anomaly detection, URL blacklisting, and other methods.
Cisco’s IoT Threat Defense portfolio offers network segmentation for IoT devices. The tool offers traffic visibility, secure access, risk assessment, incident response, and more.
The company’s Network Intuitive effort, developed using open standards, asks the device why it wants to use the network. The tool defines access control and micro-segmentation based on the intended use.
3. Security Analytics
IoT security analytics complement traditional network monitoring. Real-time data crunching detects intrusions that slip through firewalls. The best tools detect anomalies in real-time and trigger alerts. Modern AI-powered analytics tools predict future threats.
Top vendors in the space include Cisco, Indegy, Kaspersky Lab, SAP, and Senrio.
Indegy’s comprehensive Industrial Cyber Security Suite uses analytics to improve network visibility. It monitors performance, detects problem areas in real-time, and issues alerts.
4. Authentication
Robust IoT security requires authentication of legitimate users.
Traditional authentication methods such as passwords, two-factor authentication and biometrics work with IoT. But IoT authentication scenarios go beyond humans entering credentials. Many scenarios, such as embedded sensors, work machine-to-machine, without human intervention.
Baimos Technologies, Blue ID, Covisint, and Gemalto are the leading IoT authentication vendors. These solutions ensure safe authentication of a user over many devices. The best suites are cloud-based and offer authentication through mobile devices.
ForgeRock offers fine-grained authentication or push-authentication decision trees. Here, a single digital identify spreads over many sessions. Such password-less and seamless authentication enhances user experience.
5. Encryption
IoT means a constant flow of data. Many IoT endpoints lie outside the enterprise, and often in public places. The dominance of unsecured wireless traffic adds to the risk.
Encrypting data at rest and in transit between IoT edge devices and back-end systems offers reliable security.
Cryptographic algorithms render the data indecipherable to the attacker. The diversity of IoT devices and hardware profiles limits the scope to deploy standard encryption.
The trick rather lies in full encryption key lifecycle management.
Cisco, Dell, Gemalto, HPE, Lynxs, and Symantec offer effective encryption tools for IoT.
Cisco’s next-generation encryption suite co-opts elliptic curve cryptography. The tool also uses Galois/Counter Mode to speed up authentication.
The RSA algorithm is popular in many IoT applications. The RSA Archer platform, another popular tool, counters operational risk management.
6. Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
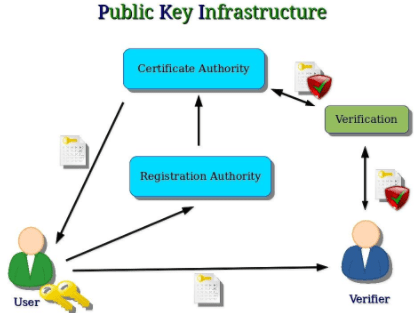
Many IoT devices have digital certificates embedded at the time of manufacture. Third-party PKI software suits may activate or deactivate such certificates, as required. These tools allow generation management and revocation or public or private keys. Effective IoT security requires X.509 digital certificates. It also requires a cryptographic key with life-cycle capabilities.
Leading PKI providers include DigiCert, Entrust Datacard, Gemalto, HPE, Symantec, and WISeKey. DigiCert co-opts PKI into the IoT framework and offers a high level of customization.
7. API security
API based security protects the integrity of data transiting between edge devices and back-end systems. REST-based APIs allow data movement between smart devices, back-end systems, and third-party applications. It detects potential threats and attacks against specific APIs.
Leading vendors in API security include Akana, Axway, CA Technologies, MuleSoft, and WS02.
Rogue Ware’s Akana Platform delivers an end-to-end API Management solution. It assists clients in developing, implementing, and managing policies.
The lack of universal IoT standards and protocols create several blind-spots. IoT is still in a fluid growth stage. As IoT-specific security threats evolve, new IoT-specific security tools will come into play.












